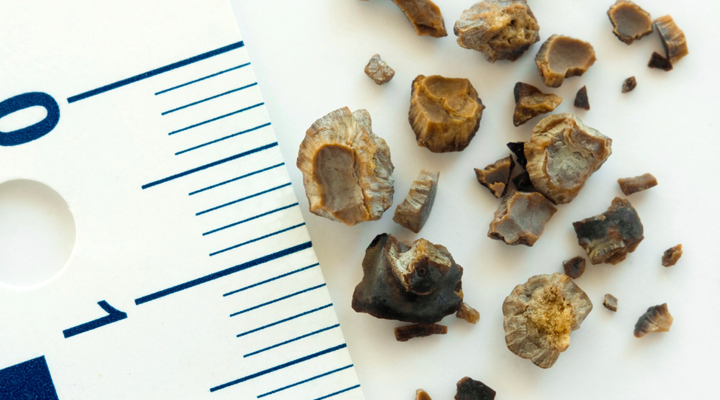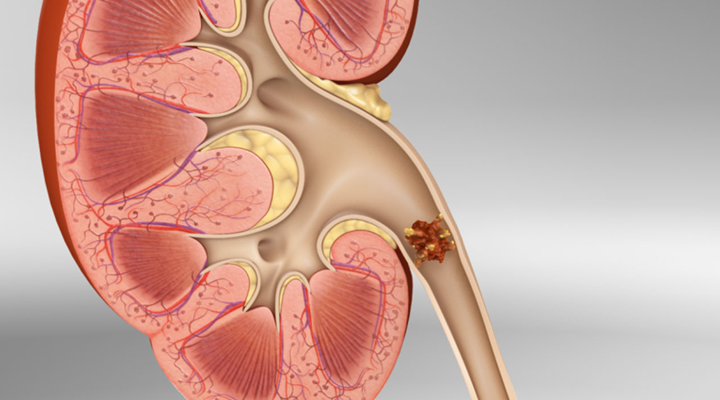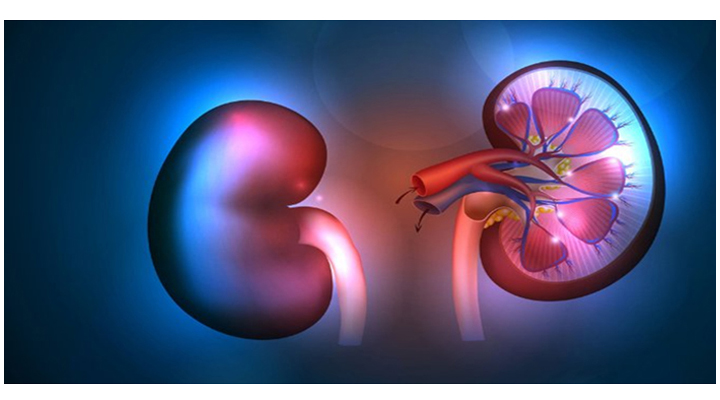
Kidney stones form when there is a decrease in urine volume and/or an excess of stone-forming substances in the urine. The most common type of kidney stone contains calcium in combination with either oxalate or phosphate. Other chemical compounds that can form stones in the urinary tract include uric acid and the amino acid cystine.
Dehydration from reduced fluid intake or strenuous exercise without adequate fluid replacement increases the risk of kidney stones. Obstruction to the flow of urine can also lead to stone formation. Kidney stones can also result from infection in the urinary tract; these are known as struvite or infection stones.
Men are especially likely to develop kidney stones, and Caucasians are more often affected than blacks. The prevalence of kidney stones begins to rise when men reach their 40s, and it continues to climb into their 70s. People who have already had more than one kidney stone are prone to develop more stones. A family history of kidney stones is also a risk factor for developing kidney stones.