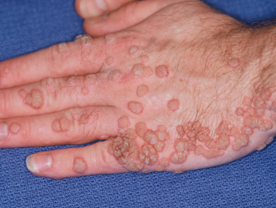
Verruca Vulgaris : Thiss is the commonest type. The lesion starts as a skin-coloured or brownish papule with an iregular surface. It is commonly seen on the hands, forearms, and face. Occasionally the warts may be located on the paronychial folds or under the nails.
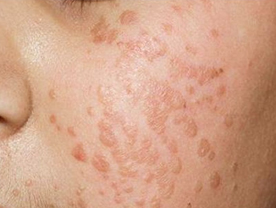
Verruca Plana : These are also skin-coloured papules which are only slightly raised from the skin surface. These are commonly seen on the face and the dorsal aspect of the hands and the forearms.
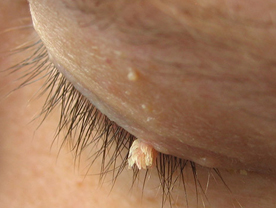
Filiform Warts : Those are finger-like projections of wany tissue commonty son on the neck and the face.
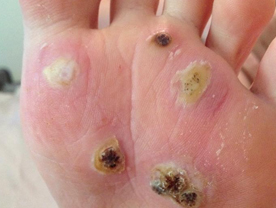
Plantar Warts :These warts usually occur as clusters of verrucous lesions on the soles and tend to grow inwards into the soles. A plantar wart may cause pain if the wart causes pressure on an underlying nerve.
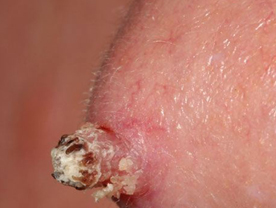
Genital Warts : These are also called condylomata acuminata and produce tungating masses of verrucous tissue on the glans in the male, vulva in the female and less commonly other areas in the genital region. These lesions tend to grow very fast during pregnancy and may cause difficulty in parturition. Genital warts are usually transmitted during sexual contact.
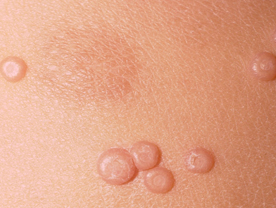
Molluscum Contagiosum : This is caused by a large sized cytoplasmic virus. Like watstis also common in children and immune compromised adults. The lesions consist of asymptomatic or compromised adults. The lesions consist of asymptomatic shiny smooth surfaced 2-10 mm sized skin-coloured or pinkish papules which may be present on any part of the body. They tend to occur in clusters. The older lesions develop an umbilication on the top of the papule. Some of the lesions can disappear spontancously but new lesions keep appearing at other sites to continue the infection. The lesions in the genital area are usually caused by sexual contact.
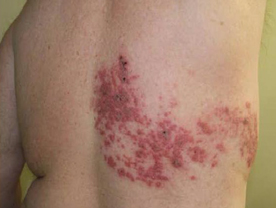
Herpes Zoster : This is caused by the varicella-zoster virus which causes chicken pox in the un-immunised individual, and herps zoster in the partially immunised individual who has acquired partial immunity to the virus during the previous attack of chicken pox. The virus gets lodged in the posterior nerve root ganglion during an attack of chicken pox, and subsequently whenever there is depression of the cell mediated immunity in the individual due to any cause the patient develops an acute eruption consisting of tense vesicles or bullae occurring in groups with erythema in the surrounding region. The eruption is characteristically limited to a single neural segment and is strictly unilateral Almost any segment of the body including the cranial nerves may be involved. The lesions tend to dry up spontaneously within 7-10 days. The most common
complication of herpes zoster consists of pain and 40 years in age this pain can persist for several months ater the eruption has healed. This is called post-herpetic
neuralgia and can be very iroublesome. In individuals having immuno-suppression, the lesions can disseminate to involve other areas of the body beyond the neural sogment. This is called disseminated herpes zoster.
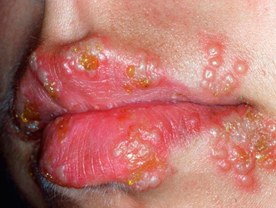
Herpes Simplex:The first attack of herpes simplex is usually very severe and s called primary herpes simplex. It manifests in the form of gingivo-stomatiuis, balano-posthitis, vulvo-vaginitis. kerato-conjunctivitis or blepharitis. The lesions consist of multiple small vesicles or superficial ulcers which may be associated with fever and malaise. The lesions tend to heal within 2 weeks even without any treatment. Occasionally, the virus may spread to the brain leading to a fatal encephalitis. Alter the first attack, in some cases, the virus gets lodged in the neural ganglion and produces recurrent attacks of herpe simplex wheneverthe virus gets reactivated. Recurrent herpes simplex is generally milder but the attacks can keep recurring at a frequency ranging from every 7-10 days to once in a year. Like the primary herpes simplex,the lesions of recurre herpes simplex are also located at the muco-cutaneous junctions.
Diagnosis :
Diagnosis: The diagnosis can be contimed by demons trating a rising titre of the antibodies to the herpes simplex vinus. This virus is of two immunologic types HSV-1 and HSV-II. Infection with HSV-I1 is usually transmitted hrough sexual contact and is therefore commonly located in the genital areas. The virus can also be cultured from the lesions

